Voltage in parallel circuits can be tricky to understand. It’s easy to think that each resistor would receive the same voltage, but this isn’t always the case. In this article, we’ll discuss how to get voltage in a parallel circuit and the math behind it.
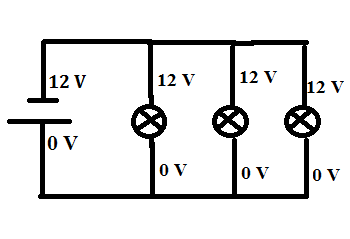
To start, let’s look at the basic components of a parallel circuit. This type of circuit consists of two or more resistors connected to a power source. The current flows through the resistors in parallel, meaning that each resistor receives the same amount of current. However, the voltage across each resistor will be different.
So, how do you calculate the voltage in a parallel circuit? The voltage across each resistor is determined by the resistance of the resistor and the power source. To calculate the voltage, you need to use Ohm’s law, which states that voltage is equal to the current multiplied by the resistance. Therefore, you can use the equation V = IR to determine the voltage in a parallel circuit. Additionally, the total voltage in the circuit is equal to the sum of the voltage across each resistor.
Understanding voltage in parallel circuits is essential when designing electrical systems. With the right calculations, you can determine the voltage across each resistor and the total voltage in the circuit. By understanding how to calculate voltage in these circuits, you can ensure that each component has the correct amount of power.
Calculating Voltage Changes In Multi Loop Circuits Study Com

Voltage In Series And Parallel Circuits Activity
Parallel Circuit Stickman Physics

Parallel Circuit That Has More Than One Path For The Cur To Pass At Least Two Branches Advantages If Part Of Is Ppt

Simple Parallel Circuits Series And Electronics Textbook

Simple Parallel Circuits Series And Electronics Textbook

Gcse Physics Electricity What Is The Voltage Across Diffe Components In A Parallel Circuit Science

Series And Parallel Circuit Calculator Dipslab Com

How To Solve Parallel Circuits 10 Steps With Pictures Wikihow

Pololu Parallel Circuits

Eet 1150 Unit 8 Parallel Circuits

Physics Tutorial Parallel Circuits

How To Calculate Voltage In Parallel Circuit Example Problems And Detailed Facts

Voltage In Series And Parallel Circuits Activity

Voltage In Parallel Circuits Sources Formula How To Add Electrical4u

Electrical Electronic Series Circuits
In A Circuit With Series And Parallel Connection Of Resistors How Should I Calculate For Voltage Drop Quora

Physics Tutorial Parallel Circuits
